Threats, Bans, and Competition: Ripple Effects in the Global Smartphone Market
Single-authored. Working Paper.
Previous title: The impact of trade wars on uninvolved countries: Evidence from the smartphone market
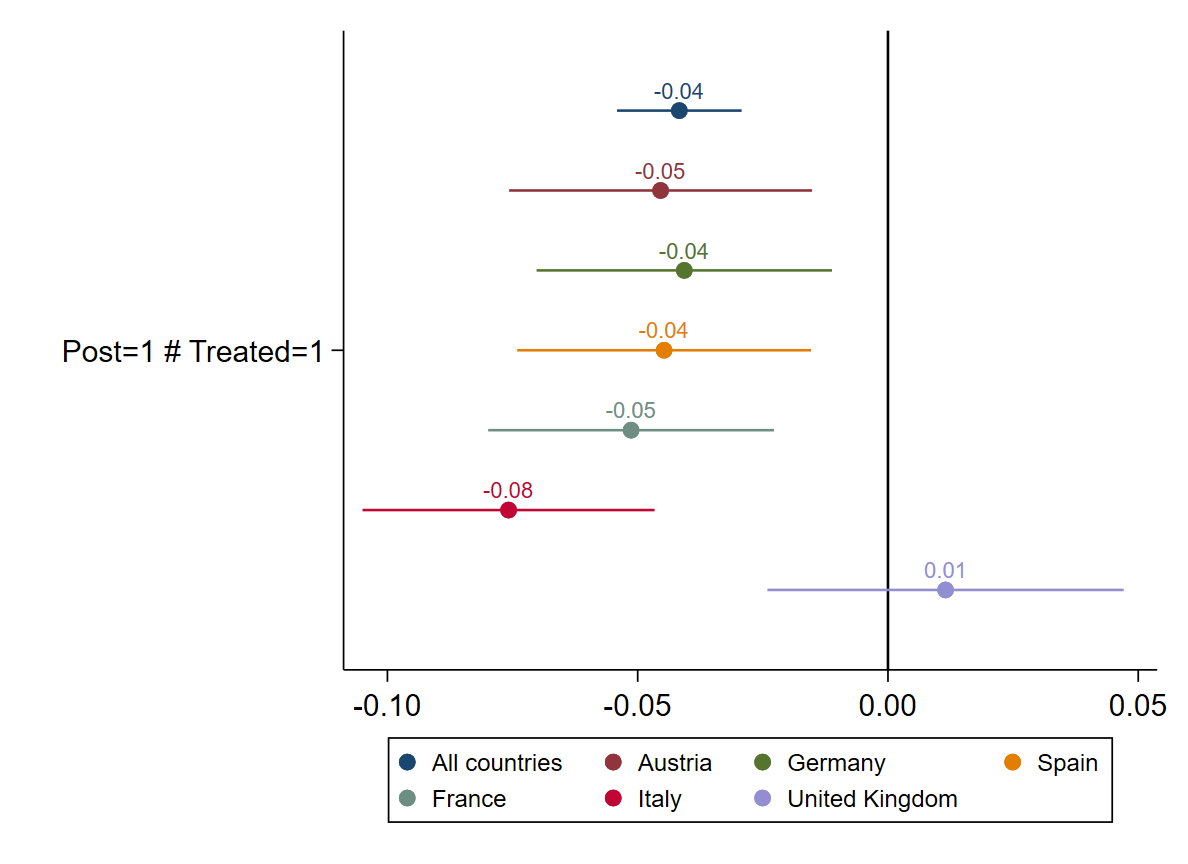
This paper investigates the ripple effects of non-tariff measures during the U.S.-China trade war on the global smartphone market, using Huawei’s placement on the U.S. Entity List in May 2019 as a natural experiment. Analyzing data on Google search volumes, daily smartphone prices for over 3,400 models, and monthly market shares across six European countries, I examine how the shock affected consumer attention, pricing, and market dynamics. My results highlight that the sanctions intensified consumer concerns, particularly regarding Huawei’s operating system, as evidenced by increased search volumes. The shock also caused a significant reduction in Huawei’s product prices, with an average decline of 4.2%, concentrated in its high-end models. However, the prices of the firm’s sub-brand Honor remained unaffected, suggesting that media attention (primarily focused on Huawei) was one of the key mechanisms affecting the demand, triggering price adjustments. In the short term, Huawei maintained its market share in Europe. However, over the long term, the forced transition to HarmonyOS in 2021, coupled with supply chain disruptions, resulted in a sharp decline in Huawei’s market position both in Europe and globally, allowing Chinese and American competitors to gain ground. Although Android’s position in the focal countries was affected, the overall impact remained moderate on the operating system market.
Period: 10.2018-10.2019